“`html
Effective Ways to Calculate Tension: Essential Methods for Accurate Results in 2025
Understanding Tension in Physics
Tension is a crucial concept in **physics tension** and plays a vital role in understanding how physical forces interact. It refers to the pulling or stretching forces transmitted through a medium, typically observed in strings, cables, and other flexible materials. To effectively **calculate tension**, one needs to appreciate its foundational principles and the methods of measurement available. Tension’s fundamental properties can be described through various **tension formulas** and **tension equations** that are vital for analyzing mechanical systems. When addressing tension in mechanics, it’s important to consider how different materials might influence the measurements and outcomes, emphasizing the significance of **tension coefficients** in the tension calculation process.
Tension Dynamics and Applications
The dynamics of tension can change dramatically based on the context. For instance, in a system with ropes or cables, such as a simple pulley, evaluating how force is distributed helps engineers and physicists understand the tension behaviors. Identifying **tension in wire** systems can reveal how tensile loads impact structural integrity. Practical applications, such as in construction, allow for effective **tension measurement** and enhance physical understanding through **tension applications**. Approved engineering standards often dictate how tension is measured and analyzed. As such, comprehending **tension principles** is crucial across various engineering fields to prevent structural failures and ensure flexibility under load.
Measuring Tension in Real Scenarios
Accurate **measuring tension** requires specific techniques and tools. Engineers often utilize tensile testing methods or **tension analysis tools** to evaluate the tensile strength of materials. Instruments like load cells or force gauges are common for precise tension quantifications. When working with structures, one might employ **tension diagrams** to visualize force distribution, thus helping in effective tension resolution. Additionally, the context in which **tension forces in structures** operate can present unique challenges, making it essential to use multiple analytical approaches for a comprehensive understanding of the tension dynamics involved.
Calculating Tension Using Different Techniques
Calculating the correct tension values can sometimes be challenging, especially in complex systems with multiple forces acting at various angles. **Tension applied force** necessitates methods that can effectively break down forces into their components. To achieve an accurate analysis, practitioners often rely on vector principles to resolve these forces systematically. Understanding changes in tension across various points can be critical for applications from engineering design to physics education, emphasizing the necessity of effective **tension analysis**.
Tension Resolution in Various Contexts
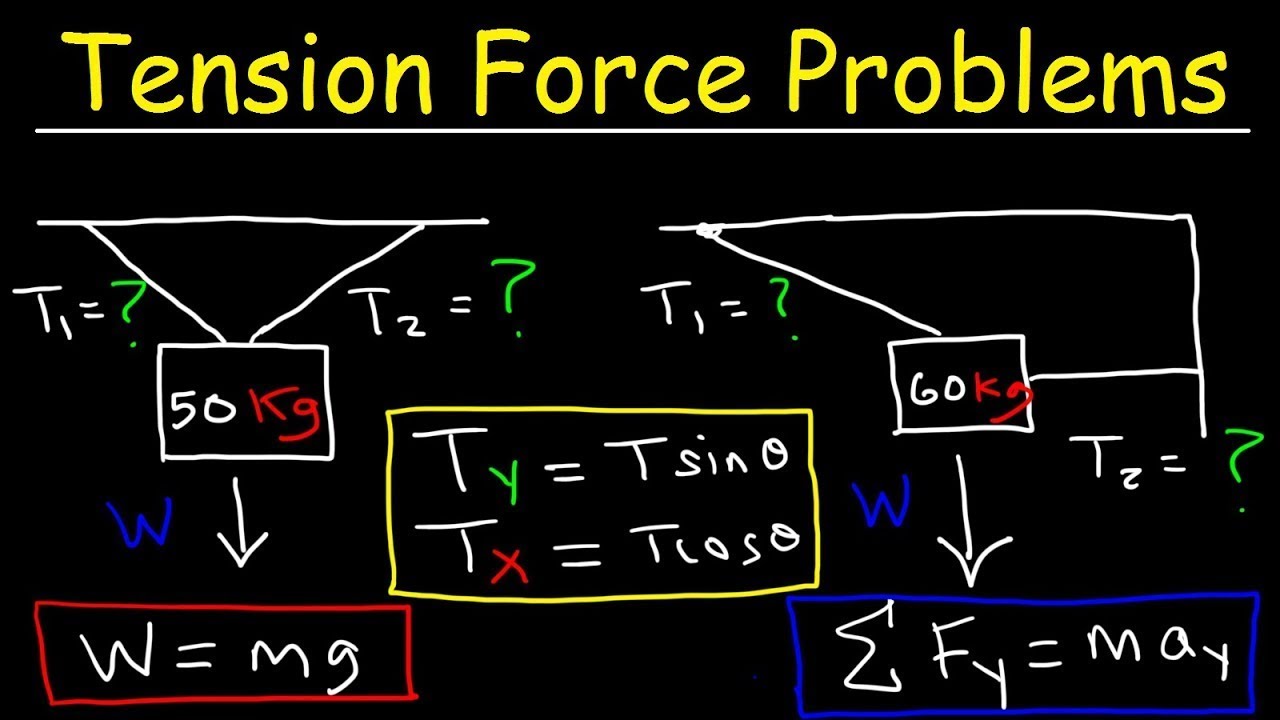
When calculating tension in cables or strings, especially in scenarios involving angles ranging from vertical to horizontal, one must apply the appropriate trigonometric principles. **Calculating tension in cables** often involves decomposing the force into vertical and horizontal components to accurately establish the equilibrium conditions. This approach ensures safety and reliability in structures where tensile strength is paramount. For instance, in construction, ensuring that tension does not exceed material limits is critical for maintaining **structural integrity**.
Applied Tension Forces: Case Study
A practical example of applied tension forces can be observed in bridge construction. Here, various cables might bear tension due to loads applied at different angles. By using **tension graphs**, engineers can model how loads distribute over those cables, allowing for detailed analysis and optimization. These calculations help prevent failure through examining **tension effects** in various materials under differing conditions. Ultimately, this meticulous process showcases the importance of systematic evaluations within engineering contexts.
Challenges and Solutions in Tension Calculations
Tension calculations often present challenges, including inaccuracies introduced with estimating loads and forces. Miscalculating tension can result in structural failures or safety hazards, particularly in uncertain environments. **Tension dynamics** provide strategic solutions ideal for grappling with such miscalculations. By applying engineering principles and tested methodologies, professionals can ensure their tension analyses lead to safe and effective outcomes in practice.
Evaluating Tension with Advanced Methods
Advanced methods in **tension analysis** involve both theoretical approaches and computational techniques. Using **numerical analysis** methods enables engineers to predict the tension and stresses in complex geometries or loading scenarios. Software simulations that analyze tension distribution can provide insights into how materials respond under different conditions, enhancing the understanding of **tension influences**. Evaluating tension through modern computational models can lead to safer and more efficient designs, especially in innovative fields such as robotics or aerospace engineering.
The Role of Tension in Design Specifications
Understanding **tension in engineering design** is paramount. Projects that require robust tensile solutions must consider safety factors and **elasticity** to accommodate shifts from static to dynamic conditions. Implementing design specifications that adequately account for tension forces ensures that structures remain reliable. This principle extends to various applications, from bridges to ropes and beyond, highlighting the ubiquitous nature of tension in mechanical systems. Regular **tensile testing** allows engineers to ensure their designs are resilient against real-world applications, ultimately optimizing tension behaviors and responses.
Key Takeaways
- Tension is a fundamental concept in physics, essential for understanding how forces interact in materials.
- Accurate tension calculations involve understanding tensile properties, effective measurement methods, and design considerations.
- Using advanced tension analysis techniques enables professionals to enhance accuracy and safety in engineering applications.
- Case studies and real-world applications demonstrate the critical role of tension in maintaining structural integrity and functionality.
- Adopting theoretical and experimental methods is paramount for ongoing improvement in tension analysis and solutions.
FAQ
1. What is the most reliable method to measure tension in cables?
The most reliable method to measure tension in cables involves using a **load cell**, which provides direct tension readings through the applied force. Other methods may include tension gauges or **tensile testing** techniques, which accurately assess how materials behave under load.
2. How does tension differ from compression?
Tension and compression are two opposing forces in mechanics. **Tension** refers to the force that **stretches** or pulls objects apart, while **compression** refers to a force that **squeezes** or pushes objects together. Understanding these forces is critical in material science and structural engineering.
3. Can tension be calculated at an angle?
Yes, tension can be calculated at an angle. This involves decomposing the force into components using **trigonometric functions**. By analyzing the angle of application, one can determine the effective tension in a system, ensuring accurate assessments of the applied forces.
4. What are common practical examples of tension in everyday life?
Common practical examples of tension in everyday life include the use of ropes in **pulley systems** or cables in suspension bridges, where load-bearing forces create prolonged tensile stress. Additionally, the strings in musical instruments also illustrate tension effects across various materials.
5. How does tensile strength affect tension calculations?
Tensile strength significantly influences **tension calculations**. Materials with high tensile strength can withstand greater forces without failure, impacting how tension is evaluated in practical applications. Engineers must consider tensile strength to ensure designs accommodate expected loads and maintain safety.
“`