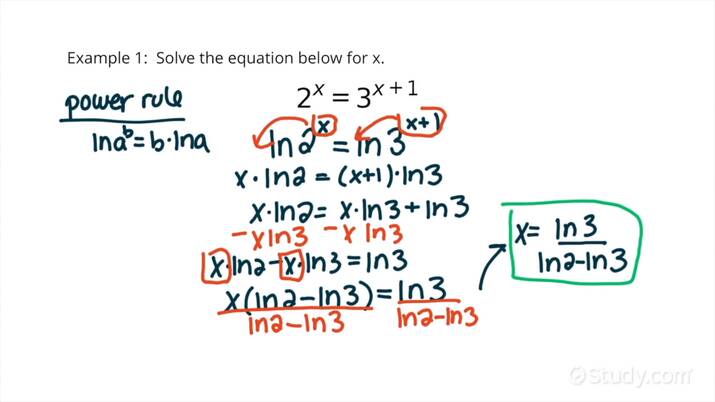How to Properly Solve Exponential Equations in 2025: Effective Strategies for Success
Exponential equations are vital components in various branches of mathematics and real-life applications. Understanding how to solve exponential equations can significantly enhance your analytical skills and provide you with tools to tackle complex problems. In 2025, educational methods and technology have evolved, making it easier than ever to approach these equations effectively. This article will explore comprehensive strategies for solving exponential equations, incorporating fundamental concepts and practical examples.
Understanding Exponential Functions
Before diving into solving exponential equations, it’s essential to grasp the concept of **exponential functions**. These functions can be characterized by an equation of the form \(y = a \cdot b^x\), where \(a\) is a constant, \(b\) is the **base of the exponent**, and \(x\) is a variable. Understanding the characteristics of these functions, such as growth and decay rates, lays the groundwork for identifying appropriate methods for solving them. For instance, in exponential growth, the function increases rapidly, often modeled in contexts such as population dynamics or finance. Conversely, **exponential decay** can be illustrated in processes like radioactive decay and depreciation. Recognizing these patterns is crucial for accurately analyzing situations and obtaining solutions to related equations.
Properties of Exponents
The **properties of exponents** are fundamental to solving exponential equations. When working with equations, you should be familiar with critical properties, such as \(b^m \cdot b^n = b^{m+n}\) and \( (b^m)^n = b^{m \cdot n}\). These properties allow for simplifications that can ease the solving process and help in **applying logarithmic transformation** when necessary. If two exponents with the same base are equal, you can deduce that their exponents must also be equal, leading to simplified equations that are often easier to solve. Utilizing these identities can be instrumental in isolating the variable and finding solutions quickly.
Applications of Exponential Equations
Exponential equations have numerous **real-world applications**, from **financial modeling** to biological population studies. Understanding how they apply to these fields can enhance your problem-solving strategies. In finance, compound interest calculations involve solving exponential equations to predict future values based on current investments and interest rates. In biology, modeling population growth could involve equations that rely on the principles of exponential growth. By grasping these applications, you bolster your ability to approach and solve relevant equations efficiently.
Common Difficulties with Exponential Equations
Many students struggle with the complexities associated with **solving exponential equations**, particularly when dealing with multiple variables or changing bases. Misunderstanding logarithmic operations often leads to errors in solutions. To navigate these challenges, it’s beneficial to engage in **practice problems** that require converting exponential forms to **logarithmic equations**. Additionally, using technology such as graphing calculators can visually represent potential solutions, making abstract concepts more tangible. By implementing these strategies, you can overcome common pitfalls in **solving for variables** in exponential equations.
Techniques for Solving Exponential Equations
There are several established techniques that can effectively aid in solving exponential equations, focusing mainly on isolating the variable or changing the equation’s form. Acquiring familiarity with these techniques is key to increasing accuracy and efficiency.
Using Logarithms
One of the most powerful tools for tackling **exponential equations** is **using logarithms**. Since logarithms are the inverse of exponentials, they can be employed to transform equations into a more manageable format. For instance, the equation \(b^x = k\) can be rewritten in logarithmic form as \(x = \log_b(k)\). This conversion allows the isolation of the variable and often leads to an easier solution method. Moreover, it’s essential to grasp the **change of base formula**, which states that \(\log_b(a) = \frac{\log_k(a)}{\log_k(b)}\), enabling you to evaluate logs with different bases effectively.
Equating Bases
Another effective strategy involves **equating bases**. If both sides of an equation can be expressed with the same base, this method allows for a straightforward way to solve for the variable. For instance, in the equation \(2^x = 8\), you recognize that 8 can be rewritten as \(2^3\), leading to \(2^x = 2^3\) and thus \(x = 3\). Utilizing this technique simplifies many equations and provides a clear path to solutions without computational complexity.
Using Graphing Techniques
Graphing is another useful approach when solving **exponential equations**. By visualizing the **exponential curve**, you can identify intersection points that represent solutions to the equation. Modern graphing tools facilitate this process, allowing you to plot equations with ease. For example, by graphing \(y = 2^x\) and \(y = 8\), you can visually observe where these functions intersect, giving you a numerical solution to the equation \(2^x = 8\). Implementing graphing techniques boosts your session’s dynamism and engagement, serving as an effective method for confirming numeric solutions.
Real-World Applications and Modeling
Understanding the implications and applications of **exponential equations** can enhance your ability to employ them in different fields. From predicting outcomes to grasping population trends, the models built using exponentials play a critical role.
Exponential Growth Models
Exponential growth models are used extensively across various disciplines, including finance, biology, and social sciences. For example, a typical **financial application** would involve calculating future investments where money grows at a constant rate. The exponential growth formula of \(P(t) = P_0 e^{rt}\) closely models this scenario, where \(P(t)\) is the future value at time \(t\), \(P_0\) is the initial investment, \(e\) is Euler’s number, \(r\) is the growth rate, and \(t\) is time. This formula illustrates how investments can exponentially grow, making it essential for anyone involved in finance to master.
Half-Life Calculations in Decay Processes
Conversely, **half-life** calculations demonstrate exponential decay, essential in fields like chemistry and biology. The half-life formula \(N(t) = N_0 \cdot (0.5)^{t/h}\), where \(N(t)\) represents quantity remaining after time \(t\), \(N_0\) is the initial quantity, and \(h\) is the half-life, is instrumental for determining how processes like radioactive decay are represented mathematically. This practical understanding allows for the modeling and prediction of decay over time, enabling accurate assessments in various scientific contexts.
Applications in Population Growth
In **population modeling**, exponential equations are frequently employed to predict future population sizes based on current figures and growth rates. Utilizing models such as the logistic growth model can provide a more realistic depiction than simple exponential growth, as they account for limiting factors in the environment. The formula for logistic growth, \(P(t) = \frac{K}{1 + e^{-r(t-t_0)}}\), incorporates carrying capacity \(K\), making it crucial for ecologists and resource managers evaluating species viability. Understanding these equations highlights the importance of mathematical modeling in ongoing ecological studies.
Key Takeaways
- Exponential equations play an essential role in finance and science.
- Using logarithms and equating bases simplifies the solving process.
- Graphing exponentially provides visual solutions and enhances understanding.
- Real-world applications, including population growth and financial modeling, illustrate the vital role of these equations.
FAQ
1. How do I convert an exponential equation into logarithmic form?
To convert an exponential equation into logarithmic form, you can follow the relationship \(b^x = k\) which becomes \(x = \log_b(k)\). This helps isolate the variable involved in your equation.
2. What are some common applications of exponential functions in finance?
In finance, exponential functions model compound interest, helping to determine future investment values. Understanding how to solve these equations is crucial for financial planning, as it reflects growth over time.
3. Why is it important to understand exponential decay?
Understanding exponential decay is vital as it applies to real-world phenomena, such as radioactive decay and depreciation in assets. Knowing how to calculate **half-life** can provide insights into current assets and resource management.
4. What role do graphing calculators play in solving exponential equations?
Graphing calculators offer a visual representation of exponential functions, helping students find solutions through intersection points. This technology enhances comprehension and enables more efficient problem-solving techniques.
5. How can models of exponential growth be corrected for limiting factors?
Models can be enhanced through logistic growth equations, which introduce parameters like carrying capacity to make predictions more realistic. This allows for understanding of real-world limitations on growth possibilities.