Essential Guide to How to Find Area of Rectangle Efficiently in 2025
Understanding the **area of a rectangle** is a fundamental aspect of basic geometry that has practical applications in numerous fields. Whether you are a student, teacher, or someone interested in geometry, mastering the *rectangle area formula* will enhance your comprehension of geometric calculations. This guide will provide you with essential techniques for **finding the area**, utilizing effective formulas, and applying these concepts to real-world situations.
Understanding Area Calculation Methods
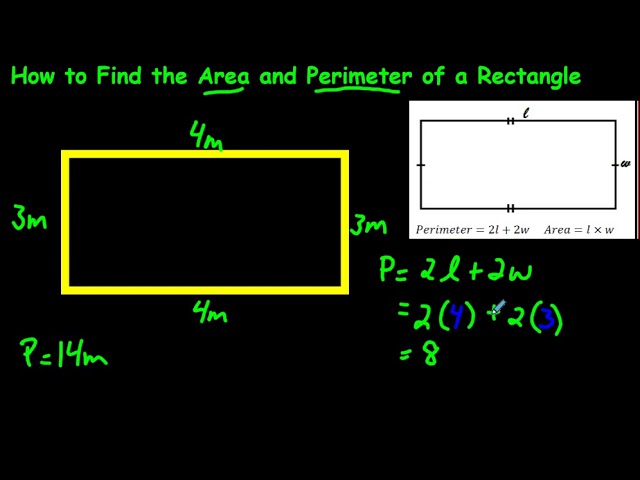
The first step in calculating the area of a rectangle is grasping its basic properties. The **rectangle area formula** states that area is calculated by multiplying the *length and width*. This relationship can be expressed as: Area = Length × Width. Each rectangle has distinct **rectangle dimensions**: the longer side is referred to as the length, and the shorter side as the width. By understanding how these properties interact, you can efficiently calculate the area. For example, if you have a rectangle with a length of 10 meters and a width of 5 meters, the area would be 10 × 5 = 50 square meters.
Rectangle Properties and Their Importance
Recognizing the **properties of rectangles** is crucial for accurate **area measurement techniques**. Rectangles are characterized by having four right angles and opposite sides that are equal in length. Understanding these attributes not only helps with geometric calculations but also assists in solving various area problems that involve complex shapes. Additionally, the concept of perimeter vs area is vital in distinguishing between covering a surface (area) and the boundary length of a shape (perimeter). A comprehensive grasp of these ideas will enhance spatial reasoning skills and facilitate geometric understanding.
Length and Width Measurement
Accurate measurements of *length and width* are essential when calculating area. Challenges often arise when performing these measurements, particularly in projects involving irregular shapes or various units of measurement. It is recommended to have the right **length measurement** tools, such as a tape measure or ruler, especially for hands-on area learning in classroom settings. Also, familiarizing yourself with **area units conversion**—like converting from square feet to square meters—can simplify comparative analysis between various surface areas in real-life applications.
Area of 2D Shapes and Advanced Areas
The area of rectangles is just one part of the larger world of **area of 2D shapes**. It is essential to compare rectangles with other shapes, such as triangles or circles, to deepen your understanding of geometric principles. Leveraging advanced area calculations can also prepare learners for higher levels of math and diverse scenarios. Additionally, various educational math resources can support you in this journey by providing **geometry lessons for kids** and envelope *basic math skills* involved in understanding shapes and their respective areas.
Adding Complexity: Multidimensional Shapes
Exploring the **calculating area of different shapes** introduces more complexity into measurements. As students progress in their geometry lessons, understanding how to visualize geometry is crucial. When facing challenges with more complex figures, like irregular shapes, students can apply multi-step area problems which enhance understanding of the basic rectangle area formula while incorporating other geometric concepts. Such cross-learning helps in establishing a strong foundation for more advanced topics in mathematics, providing critical links to fields such as architecture and engineering.
Practical Applications in Real Life
One of the best ways to reinforce learning is through practical applications, such as utilizing **rectangle measurement techniques** in everyday scenarios. For instance, understanding how to find the area when redecorating a room or farming land can illuminate the relevance and importance of the formula. *Calculating surfaces* in familiar environments, and teaching these concepts, leads to effective area instruction aligned with real-life problem-solving. In classrooms, interactive geometry tools can transform abstract concepts into engaging reality, allowing students to bridge theoretical knowledge with **effective geometry strategies**.
Geometry Basics and Teaching Techniques
As a cornerstone of mathematics, **geometry basics** form the foundation for multidimensional thinking and practical skill-building. Conducive teaching methods, such as engaging challenges and collaborative learning, can enhance understanding of measurement accuracy. For successful area instruction, consider creating hands-on area learning activities or incorporating **geometry quizzes** to engage students further. Visual representations of area can foster deeper conceptual comprehension, ultimately leading to a more profound understanding of *area in mathematics*.
Engaging Students with Area Activities
Developing interactive geometry activities and *area activities* encourages students to become more involved. Schools can design **geometry lessons** that highlight the significance of **understanding rectangles** through simple but effective methods. For example, hands-on activities like creating outlines of objects and calculating their areas can make learning captivating and informative. Also, aligning these lessons with common area mistakes enables students to identify challenges in area calculations, enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving capabilities while fostering a positive attitude towards math.
Using Software to Calculate Area
In 2025, technology plays a significant role in effective math instruction. Utilizing software to calculate area can serve as a beneficial tool for both educators and students. Advanced geometry applications allow learners to visualize concepts and understand how the rectangle area formula fits within larger mathematical frameworks. Moreover, with **educational video resources on geometry**, teaching strategies can be effectively tailored, providing versatile learning environments that cater to individual understanding and pace. Emphasizing the significance of technology integration can substantially reduce academic math struggles and bolster student engagement in geometry.
Key Takeaways
- The **rectangle area formula** is fundamental for calculating the area of rectangles.
- Properties of rectangles and accurate measurements are crucial for effective area calculations.
- Practical applications often reinforce understanding and relevance in area concepts.
- Technological tools and interactive techniques can enhance engagement and facilitate learning.
- Fostering creativity and collaboration in mathematics can improve students’ critical thinking skills.
FAQ
1. What is the primary formula for calculating the area of a rectangle?
The primary formula for calculating the area of a rectangle is Area = Length × Width. For instance, if a rectangle is 4 meters long and 3 meters wide, the area would be 4 × 3 = 12 square meters.
2. How does understanding area differ from perimeter?
The area refers to the space contained within a shape, while the perimeter is the distance around it. Understanding both concepts is critical in calculating surface space efficiently and distinguishing between covering surfaces versus measuring boundaries.
3. Are there tools available to help calculate area?
Yes, there are numerous tools and software applications specifically designed to calculate area and visualize geometric principles. Many educational platforms offer interactive geometry tools that help users accurately measure dimensions and understanding area finely.
4. How can I teach area concepts effectively?
To teach area concepts effectively, consider incorporating hands-on activities, using real-life examples, and engaging students in collaborative learning environments. Using visual aids and interactive tools can help reinforce understanding and retention of area calculation principles.
5. What are some common mistakes made when calculating area?
Common mistakes include confusing length with width, misapplying the formula, and not converting between different area units properly. Emphasizing careful measurement and ensuring students understand the fundamental math concepts can help mitigate these errors.
6. Can the area of rectangles apply to real-life scenarios?
Absolutely! The area of rectangles frequently comes into play in everyday life, such as when measuring land for landscaping, calculating how much paint is needed for a room, or determining flooring requirements.
7. Why is geometry important in mathematics?
Geometry is essential in mathematics as it helps build spatial reasoning skills, aids in the understanding of diverse shapes and their properties, and supports problem-solving strategies applied in various fields like architecture, engineering, and more.